Vmax, or maximum velocity, is a crucial parameter in enzyme kinetics, representing the highest rate achieved by a reaction at saturating substrate concentrations. Understanding how to determine Vmax is essential for characterizing enzyme activity and understanding biological processes. This article explains how to find Vmax using the Michaelis-Menten equation and the Lineweaver-Burk plot.
The Michaelis-Menten equation describes the relationship between the reaction rate (V) and substrate concentration ([S]):
V = Vmax * [S] / (Km + [S])Where:
- Vmax is the maximum velocity
- [S] is the substrate concentration
- Km is the Michaelis constant, indicating the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax.
One common method to determine Vmax is using the Lineweaver-Burk plot. This involves plotting the reciprocal of the reaction rate (1/V) against the reciprocal of the substrate concentration (1/[S]). The resulting graph is a straight line with the following equation:
1/V = (Km/Vmax) * (1/[S]) + 1/VmaxThis equation resembles the equation of a straight line (y = mx + c), where:
- y = 1/V
- x = 1/[S]
- slope (m) = Km/Vmax
- y-intercept (c) = 1/Vmax
By plotting 1/V against 1/[S], you can determine the y-intercept. The reciprocal of the y-intercept gives the value of Vmax. For instance, if the y-intercept is 0.4767, then Vmax = 1/0.4767 = 2.10 mM s-1. The slope of the line can then be used to calculate Km.
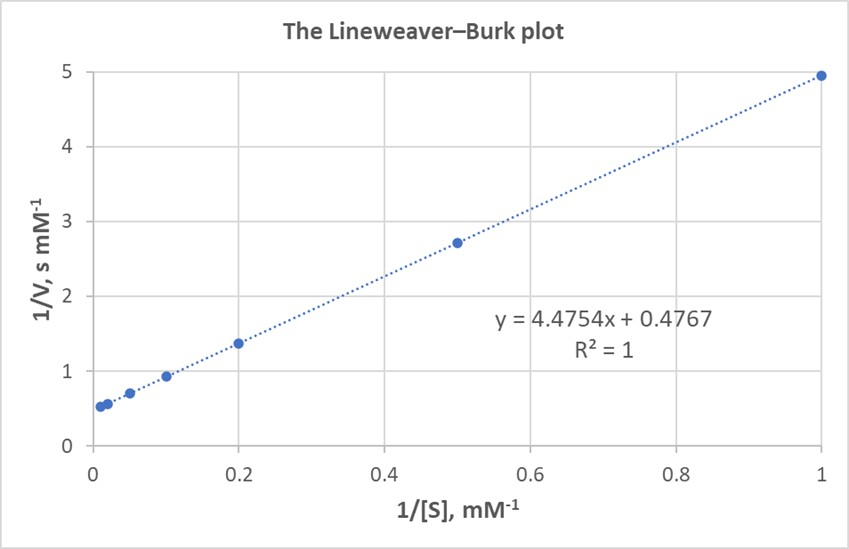 Lineweaver-Burk Plot Example
Lineweaver-Burk Plot Example
This graph shows a Lineweaver-Burk plot where the y-intercept allows for the determination of Vmax.
Finding Vmax allows for calculating the turnover number (kcat) of an enzyme, representing the number of substrate molecules converted into product per enzyme molecule per unit time. This is calculated using the following equation:
kcat = Vmax / [E]TWhere [E]T is the total enzyme concentration. Knowing kcat helps in comparing the efficiency of different enzymes or the same enzyme under different conditions.
In summary, determining Vmax is crucial for understanding enzyme kinetics. Utilizing the Lineweaver-Burk plot by graphing the reciprocals of reaction rate and substrate concentration offers a straightforward method to calculate Vmax from experimental data. The derived Vmax value can be further used to calculate kcat, providing insight into enzyme efficiency.
Reference:
- George Edward Briggs and John Burdon Sanderson Haldane, “A Note on the Kinetics of Enzyme Action,” Biochem. J. 1925, 19(2), 338-339 (DOI: 10.1042/bj0190338).
