A failing CDI box can be a major headache for any motorcycle owner. Understanding the wiring diagram, particularly for a common 6-pin CDI box, is crucial for diagnosing and resolving electrical issues. This article provides insight into common CDI problems, testing procedures, and wiring diagrams to help you get your bike back on the road. We’ll also explore the compatibility of Zongshen CDI units with certain Yamaha models.
Common CDI Box Issues and Troubleshooting
CDI boxes, especially in Chinese motorcycles, are known to fail. A spare CDI unit is invaluable for troubleshooting. If your bike experiences electrical problems, swapping in a known good CDI box can quickly determine if the CDI is the culprit. Other components, like the stator and pickup coil, can also fail, especially after prolonged exposure to hot engine oil. Over time, the oil can degrade the varnish on the wire coils, leading to short circuits.
If a spare CDI doesn’t fix the problem, testing the stator and pickup coil resistance is the next step. A multimeter is essential for this task. Refer to your motorcycle’s specific service manual for the correct resistance values.
Zongshen CDI Compatibility with Yamaha Motorcycles
Interestingly, Zongshen CDI boxes, stators, and pickup coils are often compatible with various Yamaha models, including the XT200, TW200, XT225, TT-R225, and TT-R230. This compatibility offers a cost-effective alternative to expensive OEM Yamaha parts. For example, replacing a Yamaha stator and pickup coil can cost over $500, while comparable Zongshen parts are significantly cheaper.
The physical dimensions of the Zongshen components often allow for a direct replacement within the Yamaha stator cover. However, you may need to adapt the wiring harness. The Zongshen CDI typically uses a 6-pin connector similar to those found on Lifan 150cc pit bikes. Wiring harnesses for these CDI units are readily available online.
Understanding the 6-Pin CDI Wiring Diagram
A typical 6-pin CDI wiring diagram will include connections for:
- Power: From the battery or charging system.
- Ground: Completes the electrical circuit.
- Pulse: Signal from the pickup coil, triggering the CDI to fire the spark plug.
- Ignition Coil: Sends high voltage to the spark plug.
- Kill Switch: Cuts off the ignition.
- Source Coil: Provides power to the CDI.
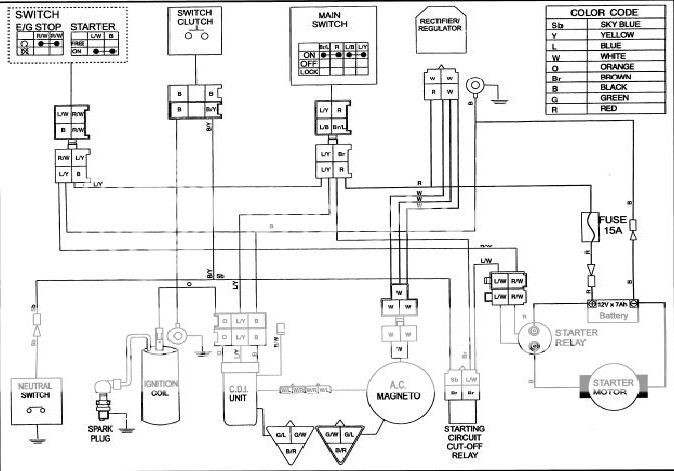 Yamaha TT-R225 wiring diagram showcasing the connections to the CDI unit and other components
Yamaha TT-R225 wiring diagram showcasing the connections to the CDI unit and other components
Using a wiring diagram, trace each wire to ensure proper connections. A misplaced wire can prevent the engine from running or cause significant damage.
Conclusion
Understanding your motorcycle’s electrical system, particularly the CDI box and its associated components, is essential for maintenance and repair. Using a 6 pin CDI wiring diagram, coupled with basic troubleshooting techniques, can help you identify and resolve electrical issues effectively. Remember to consult your motorcycle’s service manual for specific wiring diagrams and resistance values. The compatibility of Zongshen parts with certain Yamaha models offers a budget-friendly solution for common electrical problems.

