When your car starts showing electrical problems such as dim headlights or a consistently dead battery, a faulty alternator is often suspected. Before rushing to a mechanic, you might wonder: can a car diagnostic tool detect a bad alternator? The answer is generally yes, with some important considerations.
As an experienced auto repair expert at carscannertool.store, I’ll explain how an OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT1009, can be instrumental in diagnosing alternator issues. We’ll explore the process, its limitations, and how to use these tools effectively to assess your alternator’s health.
Understanding Your Alternator’s Crucial Role
The alternator is a vital component of your vehicle’s electrical system. Think of it as the heart of your car’s electrical system, constantly generating power while the engine is running. This power is essential for operating various electrical components, from your headlights and infotainment system to critical engine management systems.
A healthy alternator ensures your battery remains charged and all electrical systems function correctly. However, alternators don’t last forever. Signs of a failing alternator can include flickering or dimming headlights, slow engine cranking, warning lights on your dashboard, or frequent dead batteries. If your alternator fails, your car will eventually rely solely on the battery, which will quickly drain and leave you stranded. Recognizing these early warning signs can save you from inconvenient breakdowns and costly repairs down the road.
How Car Diagnostic Tools Help Identify Alternator Problems
An OBD2 scanner, particularly advanced models like the Foxwell NT1009, is a valuable tool for diagnosing various car problems, including potential alternator issues. These tools work by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in your car’s computer when a system malfunction is detected. While a car diagnostic tool won’t directly declare “bad alternator,” it can provide crucial clues and point you in the right direction.
When it comes to alternators, a diagnostic scan can identify related electrical issues. For example, codes indicating low voltage (like P0562) or problems within the alternator field control circuit (such as P0622) are strong indicators of alternator malfunction. These codes, along with live data monitoring, can help you determine if the alternator is indeed the source of the problem or if further investigation into other components is needed.
Step-by-Step Guide: Using a Car Diagnostic Tool for Alternator Checks
To effectively use a car diagnostic tool to check for alternator problems, follow these steps:
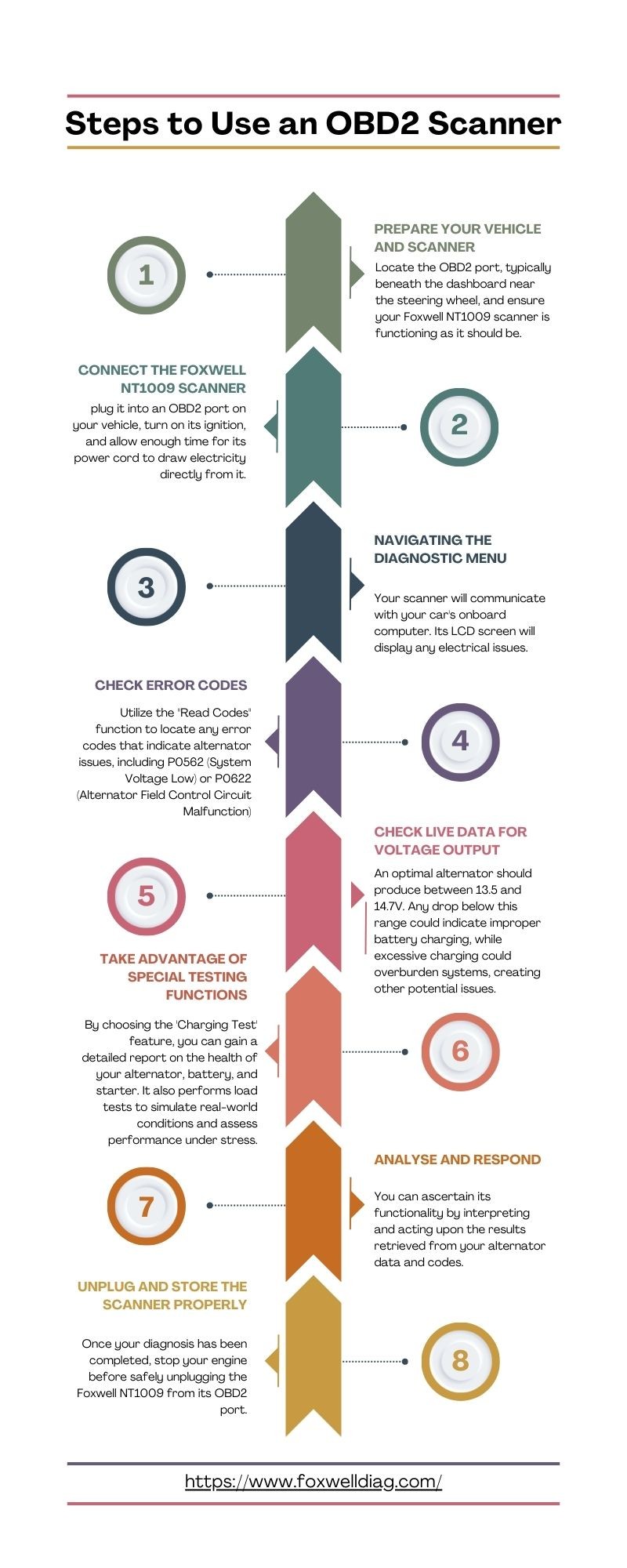
1. Vehicle Preparation and Scanner Readiness
Begin by ensuring your vehicle is prepared for the diagnostic process. Turn off all unnecessary electrical loads such as headlights, radio, and air conditioning. This minimizes electrical draw and provides a more accurate reading. Locate your car’s OBD2 port, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Make sure your Foxwell NT1009 or chosen OBD2 scanner is powered on and functioning correctly.
2. Connecting Your Diagnostic Scanner
Plug the Foxwell NT1009 securely into the OBD2 port. Turn your car’s ignition to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine yet. This allows the scanner to draw power from the car and establish communication with the vehicle’s computer system. Allow a few moments for the scanner to initialize and connect to all relevant systems.
3. Navigating to the Diagnostic Menu
Once connected, navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Diagnostic” or “Scan” section. Select this option. You may be prompted to enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year for more accurate diagnostics. The scanner will then begin communicating with your car’s onboard computer to retrieve diagnostic information.
4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use the “Read Codes” or “Trouble Codes” function on your scanner. This will display any stored DTCs. Look for codes that are related to the charging system or voltage issues. Pay close attention to codes like:
- P0562 (System Voltage Low): This code often indicates that the system voltage is lower than expected, which can be caused by a failing alternator not producing enough power.
- P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction): This code points to a problem within the alternator’s control circuit, directly suggesting an alternator issue.
While these codes don’t definitively say “bad alternator,” they are strong indicators that warrant further investigation of the alternator and charging system.
5. Analyzing Live Data for Voltage Output
A crucial step in alternator diagnosis using a diagnostic tool is monitoring live data. Select the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on your Foxwell NT1009. Start your car’s engine. Look for voltage readings within the live data stream, often labeled as “Battery Voltage” or “System Voltage.”
A healthy alternator should typically produce a voltage output between 13.5 and 14.7 volts when the engine is running. Readings below this range may indicate the alternator is not charging the battery effectively. Conversely, excessively high voltage can also be problematic, suggesting overcharging, though low voltage is more commonly associated with a failing alternator.
To further assess the alternator’s performance under load, turn on various electrical accessories such as headlights, air conditioning, and the radio. Observe the voltage readings as you add electrical load. A significant drop in voltage under load further suggests the alternator is struggling to keep up with the electrical demands, indicating a potential alternator problem.
6. Utilizing Special Testing Functions
Some advanced diagnostic scanners like the Foxwell NT1009 offer specialized testing functions for the charging system. Explore your scanner’s menu for options like “Charging System Test” or “Alternator Test.” These tests often perform a more in-depth analysis of the alternator, battery, and starter, sometimes including load tests to simulate real-world driving conditions and assess performance under stress. These specialized tests can provide a more comprehensive report on your alternator’s health.
7. Interpreting Results and Taking Action
Carefully analyze the data from error codes and live voltage readings. If you retrieved codes like P0562 or P0622, and if your live voltage readings are consistently outside the normal range (especially below 13.5V), it strongly suggests an issue with your alternator.
Based on these findings, you can decide on the next steps. If the diagnostic tool points towards an alternator problem, it’s advisable to perform further tests, such as a multimeter test or a professional load test, or consult a qualified mechanic for a definitive diagnosis and repair.
After performing any repairs or replacements, you can use your diagnostic scanner to clear the stored DTCs.
8. Disconnecting and Storing the Scanner
Once you have completed your diagnosis and any necessary code clearing, turn off your car’s engine and ignition. Safely disconnect the Foxwell NT1009 from the OBD2 port. Store your scanner in a clean, dry place, ready for future use.
Alternative Methods for Alternator Testing
While a car diagnostic tool is helpful, it’s not the only method to test your alternator. Here are a couple of alternative approaches:
1. Multimeter Test: A multimeter is a simple and effective tool for basic alternator testing. With the engine running, connect the multimeter to your car battery terminals. A reading between 13.5 and 14.7 volts generally indicates the alternator is functioning correctly. Readings outside this range suggest a potential alternator issue.
2. Load Test: A load test provides a more thorough assessment of the alternator’s capacity. This test measures the alternator’s output under increased electrical load. Load testing can be performed using specialized equipment or by a professional mechanic. It reveals how well the alternator maintains voltage and current output when various electrical components are activated, providing a more comprehensive picture of its health.
Conclusion: Car Diagnostic Tools and Alternator Diagnosis
In conclusion, yes, a car diagnostic tool can detect a bad alternator, albeit indirectly. Tools like the Foxwell NT1009 are invaluable for identifying potential alternator problems by reading trouble codes and monitoring live data, particularly voltage output. They serve as an excellent first step in diagnosing electrical issues and can provide crucial information to guide your troubleshooting process.
However, it’s important to remember that a diagnostic scan is not always a definitive alternator test. In some cases, further testing with a multimeter or a load test might be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Using a car diagnostic tool in conjunction with other testing methods provides a more comprehensive approach to alternator diagnosis, enabling you to address car electrical issues effectively and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Regular use of a diagnostic scanner for vehicle maintenance can help keep your car’s electrical system in good condition and prevent costly repairs down the line.
FAQs
Can you test an alternator with a car diagnostic tool?
Yes, a car diagnostic tool is a valuable aid in testing an alternator. It can read error codes related to charging system malfunctions and monitor live voltage data, helping you assess the alternator’s performance. However, it may not provide a direct “bad alternator” diagnosis and might require supplementary tests.
Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
Potentially, yes. A failing alternator can trigger related trouble codes during a scan, such as codes indicating low system voltage or issues within the alternator circuit. While the scan might not explicitly state “bad alternator,” these codes act as red flags, signaling a problem that warrants further investigation of the alternator.
Is there a specific OBD code for alternator failure?
While there isn’t a single OBD code that says “alternator failed,” certain codes are strongly associated with alternator problems. Common codes to watch out for include P0562 (System Voltage Low) and P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction). These codes strongly suggest that your alternator is not operating correctly and requires attention.