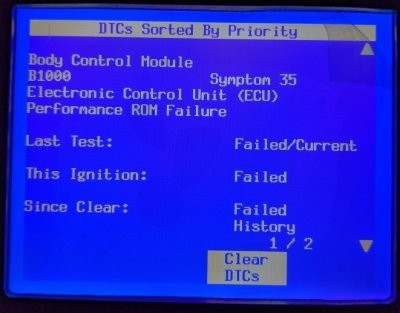
The B1000 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) can be a source of confusion for vehicle owners. This code indicates an ECU (Engine Control Unit) malfunction, specifically related to the performance ROM (Read-Only Memory). While the B1000 code itself doesn’t pinpoint the exact problem, understanding its potential causes and troubleshooting steps can help you address the issue effectively.
What Does the B1000 Ecu Malfunction Code Mean?
The B1000 code signals a problem within the ECU’s internal memory. Symptom code 35, often associated with B1000, points to a ROM failure. The ROM stores crucial operating instructions for the ECU, and a malfunction can disrupt various vehicle functions. This could manifest as performance issues, drivability problems, or even prevent the vehicle from starting. However, it’s important to note that a B1000 code might not always result in noticeable symptoms.
Possible Causes of a B1000 ECU Malfunction
Several factors can contribute to a B1000 code:
- Faulty ECU: The most common cause is a defective ECU that requires replacement or repair. Internal hardware issues within the ECU can corrupt the ROM or prevent it from functioning correctly.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring in the ECU harness can disrupt communication and trigger the B1000 code. Inspecting the harness for loose connections, broken wires, or signs of corrosion is crucial.
- Software Issues: In some cases, corrupted or outdated ECU software can lead to a B1000 error. Reflashing or updating the ECU software might resolve the issue. A failed software update or the installation of a custom tune could also be contributing factors.
- Low Battery Voltage: A weak or failing battery can cause voltage fluctuations that affect the ECU’s operation and potentially trigger a B1000 code. Ensuring a healthy battery is essential for proper ECU function.
Troubleshooting the B1000 Code
Diagnosing a B1000 code requires a systematic approach:
- Check for Other Codes: Scan the vehicle for other DTCs that might provide clues related to the B1000 code.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Thoroughly examine the ECU wiring harness for any damage or corrosion. Clean and tighten connections as needed.
- Battery Voltage Test: Verify that the battery voltage is within the specified range. A low or fluctuating voltage can impact ECU performance.
- Software Update/Reflash: Consult with a qualified technician to determine if a software update or reflash is necessary for the ECU. This process might require specialized equipment and software access.
- ECU Testing/Replacement: If other troubleshooting steps fail to resolve the issue, the ECU itself might need testing or replacement. This is often best handled by a professional automotive technician with access to diagnostic tools.
Conclusion
A B1000 ECU malfunction code signifies a potential problem within the engine control unit’s internal memory. While it can be daunting, understanding the possible causes and following a structured troubleshooting process can help pinpoint the source of the issue. Remember, consulting a qualified mechanic with diagnostic expertise is always recommended for complex electrical problems like a B1000 code. They can accurately diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate course of action, whether it’s repairing wiring, updating software, or replacing the ECU.