Most drivers simply want their car’s air conditioning to blast cold air on a hot day. Understanding how an HVAC tool for car works in conjunction with the entire system, however, can be incredibly beneficial, especially when issues arise. While this article will primarily explain the car AC system itself, we’ll touch upon how diagnostic tools, specifically HVAC tools, play a crucial role in maintaining and repairing these systems.
Car air conditioning systems are marvels of engineering, using refrigerant in liquid and gaseous states to pull heat and humidity from your car, leaving you cool and comfortable. The refrigerants have evolved over time, moving from R-12 (Freon) to R-134a, and now increasingly to R-1234yf, which is more environmentally friendly.
The core of your car’s AC includes components like the compressor, condenser, dryer, metering device, and evaporator, each vital to the cooling process. Common AC problems often stem from leaks, which can cripple the compressor, or blockages in the condenser due to road debris. Automotive technicians utilize specialized HVAC tools to pinpoint and fix these issues, making this expertise indispensable in auto repair.
If you’re curious about the inner workings of your car’s AC and how HVAC tools for cars assist in their upkeep, keep reading to delve into AC theory, components, operation, and the tools used for diagnostics.
Decoding Car AC Operation: The Refrigeration Cycle
The magic behind your car’s AC lies in manipulating refrigerant between liquid and gas. This transformation is the key to heat absorption and humidity removal, resulting in the cool, dry air you enjoy. The system meticulously controls pressure and temperature to achieve these state changes in the refrigerant. To understand how an HVAC tool for car works in this context, imagine it as a doctor’s stethoscope for your AC, helping to listen to the system’s pressure and temperature “heartbeat.”
Refrigerant Evolution in Car AC Systems
Let’s take a quick look at the refrigerants used in car ACs. Older systems relied on R-12 (Freon), a highly effective but environmentally damaging CFC. In the mid-1990s, the industry shifted to R-134a, an HFC refrigerant that’s ozone-friendly. Today, R-1234yf is gaining traction, especially in Europe and likely soon in the US, due to its lower greenhouse gas impact. When your AC needs a recharge, technicians use HVAC tools for cars to safely handle and replenish these refrigerants.
Key Components of a Car AC System and How HVAC Tools Interact
Let’s explore the main players in your car’s AC system and consider how HVAC tools for cars are used in their diagnosis and maintenance.
Compressor
- The compressor is the AC system’s powerhouse, separating the low-pressure and high-pressure sides.
- It takes in low-pressure refrigerant gas and squeezes it into a hot, high-pressure gas.
- Driven by the serpentine belt at the front of the engine.
- HVAC tools like manifold gauges are connected to service ports near the compressor to measure system pressures, crucial for diagnosing compressor performance.
Condenser
- The condenser cools down the high-pressure refrigerant gas, turning it into a liquid.
- It works like a radiator, using airflow (from a fan or vehicle movement) to dissipate heat.
- Located at the front of the car, behind the grille.
- Thermal imaging tools, while not strictly HVAC tools, can help identify condenser inefficiencies by showing temperature variations across its surface.
Dryer (Receiver/Drier)
- The dryer removes moisture from the refrigerant using a desiccant.
- It also filters out contaminants.
- Positioned on the high-pressure side, between the condenser and metering device.
- Visual inspection and pressure readings using manifold gauges can indicate a blockage within the dryer, though it’s often replaced as part of routine maintenance or system repair when using HVAC tools for cars.
Metering Device (Expansion Valve or Orifice Tube)
- This device reduces refrigerant pressure drastically, causing a rapid temperature drop.
- The refrigerant remains a liquid after passing through it.
- Located on the high-pressure side, between the dryer and firewall.
- Superheat and subcooling calculations, done with temperature and pressure readings from HVAC tools, help assess the metering device’s performance.
Evaporator
- Here, the liquid refrigerant turns back into a gas, creating a cooling effect.
- Cabin air passes over the evaporator, getting cooled and dehumidified.
- The only component inside the passenger compartment, behind the dashboard.
- Temperature probes and airflow meters, sometimes part of advanced HVAC diagnostic tool sets, can verify evaporator efficiency.
Refrigerant Journey: A Cycle of Cooling
- Refrigerant enters the compressor as a low-temperature/low-pressure gas.
- Exits the compressor as a high-temperature/high-pressure gas.
- Cools and condenses to a liquid in the condenser, still at high pressure.
- Passes through the receiver/dryer for moisture removal.
- Pressure drops significantly at the expansion valve.
- Turns back into a gas in the evaporator, absorbing heat and cooling the cabin air.
Visualizing the System
Here’s a diagram illustrating the AC system and component connections:
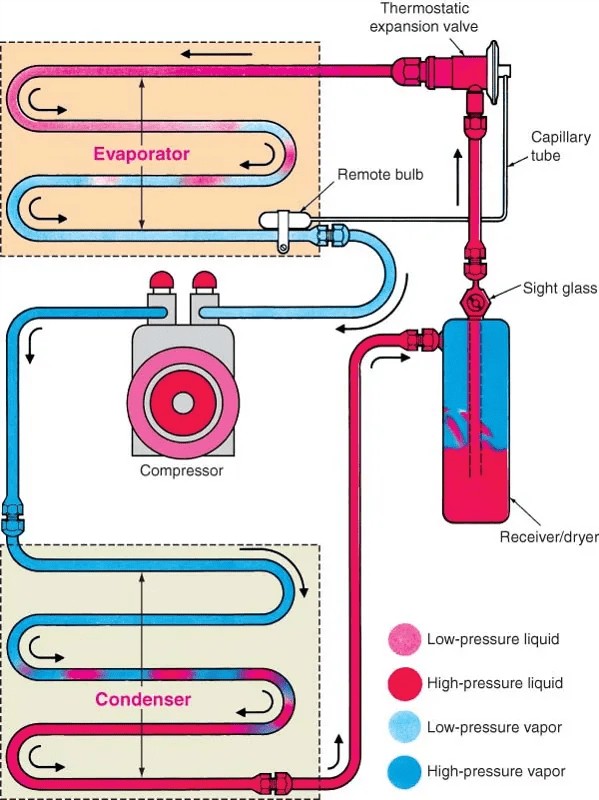 Car AC System Diagram showing Compressor, Condenser, Dryer, Expansion Valve, and Evaporator
Car AC System Diagram showing Compressor, Condenser, Dryer, Expansion Valve, and Evaporator
Common AC System Problems and the Role of HVAC Tools
AC systems are sealed and pressurized, so leaks and contamination are major concerns. Simply adding refrigerant to a leaking system is a temporary fix at best. HVAC tools for cars are essential for proper diagnosis and repair.
Leaks are a prime culprit, potentially damaging the compressor if refrigerant levels get too low. Compressors are usually not repairable and are costly to replace. Electronic leak detectors and UV dye kits, common HVAC tools, help technicians find even tiny refrigerant leaks.
Condenser airflow is also crucial. Road debris and dirt can obstruct airflow, leading to system malfunction. Regular inspection and cleaning are important. While not directly an HVAC tool, a pressure washer can be used carefully to clean the condenser fins.
HVAC Tools and Your Auto Repair Career
With AC now standard in nearly every car, AC system repair is a constant need. Auto technicians routinely diagnose and fix AC issues, from warm air complaints to strange noises and leaks. Mastering the use of HVAC tools for cars is a core skill for any successful automotive technician.
AC System FAQs & The Tools That Help Answer Them
How does a car air conditioner work, and what HVAC tools help understand it?
The AC cools air using refrigerant cycled by the compressor. Manifold gauges (HVAC tool) monitor pressures, revealing compressor and overall system health.
What are the main AC components, and how do HVAC tools diagnose them?
Key parts are the compressor, condenser, evaporator, dryer, and expansion valve. HVAC tools like manifold gauges, thermometers, and leak detectors are used to assess each component’s function.
How does refrigerant cool the air, and how do HVAC tools verify this?
Refrigerant absorbs heat as it evaporates in the evaporator. HVAC tools help measure system pressures and temperatures, confirming proper refrigerant state changes and cooling efficiency.
Pursue Automotive Technician Training and Master HVAC Tools
Interested in a career as an auto technician? Training programs equip you with skills in all vehicle systems, including AC and the essential HVAC tools for cars.
Gain hands-on experience and knowledge to launch your career in less than a year.
Hands-on training. Get practical experience with industry-standard equipment.
Start your career now. Classes begin frequently.
Learn more and get started!
Related Articles
[
How Long Does It Take to Become an Automotive Mechanic?](/blog/education/automotive-technician-career)How long does it take to become an auto mechanic? Explore this role and how to pursue a career in the industry with training from UTI!
[
What Is an Automotive Service Writer and What Do They Do?](/blog/automotive/automotive-service-writer)Learn the automotive service writer job description, how to become a service writer, and where the career can take you.
[
The Automotive Technician Shortage: What Does This Mean for Your Career?](/blog/automotive/automotive-tech-shortage)You’ve heard about the automotive technician shortage…but what does this mean for you?
1 ) UTI is an educational institution and cannot guarantee employment or salary.
2 ) For program outcome information and other disclosures, visit www.uti.edu/disclosures.
7 ) Some programs may require longer than one year to complete.
Universal Technical Institute of Illinois, Inc. is approved by the Division of Private Business and Vocational Schools of the Illinois Board of Higher Education.
