Have you ever faced perplexing electrical issues in your car, like flickering lights, sensor malfunctions, or even more mysterious problems? Pinpointing and resolving these issues used to be a daunting task, but not anymore!
With a digital circuit identification tool designed for cars, diagnosing electrical problems has become significantly easier, even for those with limited experience. This guide will show you how to effectively use these tools to troubleshoot like a seasoned expert, even if you’re starting from scratch.
Understanding the Circuit Identification Tool for Cars
A circuit identification tool for cars, often referred to as a digital car circuit scanner, is specifically engineered to quickly and accurately diagnose electrical problems within your vehicle’s intricate wiring system.
Imagine it as a specialized flashlight for your car’s electrical system. It illuminates problem areas much faster and more precisely than manually tracing wires or relying on guesswork.
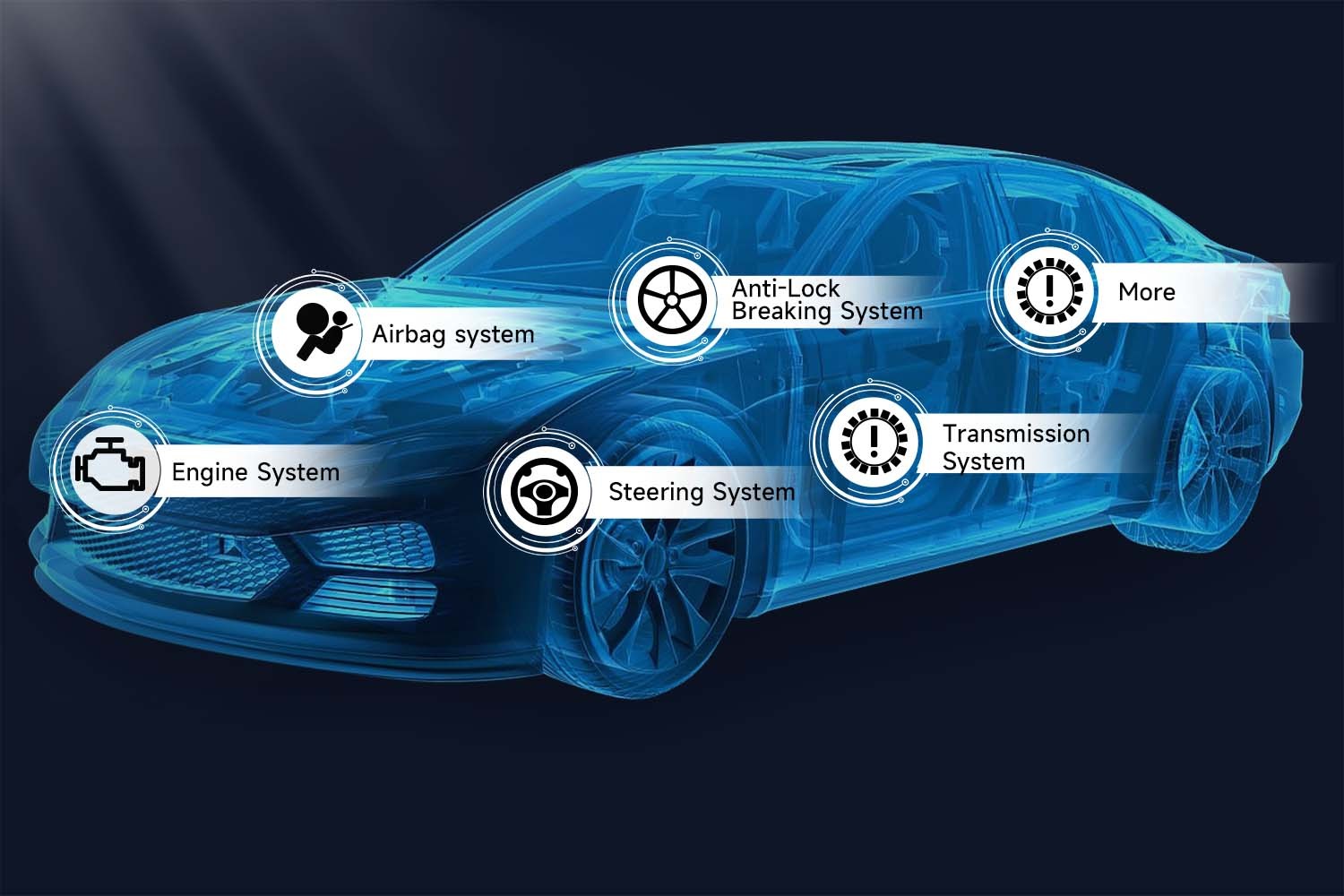
Modern vehicles are packed with electrical components, from vital engine sensors to complex entertainment systems. These components are interconnected through complex circuit networks, making issue diagnosis challenging.
A circuit identification tool simplifies this process by performing tests on voltage, continuity, and signal flow. This provides a clearer picture of where electrical faults might be located.
Essential Features and Functions of Circuit Identification Tools
To maximize the benefits of a car circuit identification tool, understanding its core functions is crucial. While features may vary across models, most tools offer these key capabilities:
- Voltage Testing: This function measures if a circuit is receiving the correct electrical pressure. It’s akin to checking water pressure in a hose; pressure that is too high or too low signals a potential problem. In car circuits, correct voltage is vital for component operation.
- Continuity Testing: Continuity testing verifies if an electrical circuit is complete and unbroken. Think of it like a string of Christmas lights; if one bulb is broken, the circuit is incomplete. This test helps find breaks in your car’s wiring.
- Short Circuit Detection: Short circuits occur when electricity deviates from its intended path, often due to damaged wiring. Short circuit detection helps quickly locate these unintended pathways, saving you from manually inspecting every wire.
- Signal Tracing: This feature allows you to follow an electrical signal from its origin to its destination, ensuring it reaches the intended component without interruption. It’s like following a trail of breadcrumbs to ensure the signal’s integrity.
Each of these functions is designed to address different types of electrical problems. Familiarity with these features is the first step toward becoming proficient in automotive electrical troubleshooting.
Step-by-Step Guide: Using a Circuit Identification Tool on Your Car
The Foxwell GT60 serves as an excellent example of a user-friendly circuit identification tool, incorporating all the essential functions discussed. Designed for both beginners and professionals, it simplifies car diagnostics. Here’s a guide on using it to identify and fix electrical issues in your vehicle:
Step 1: Powering Up and Connecting Your Tool
Before starting, ensure your GT60 is adequately charged or connected to an external power source. The device’s large touchscreen, while convenient, can quickly deplete battery power. For extended diagnostic sessions, it’s advisable to keep it plugged in.
Locate your car’s OBD2 port, usually situated under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Connect the GT60’s OBD2 cable to this port. Upon powering on, the tool will automatically recognize your car’s make, model, and year, streamlining the diagnostic process for quick and accurate results.
Step 2: Selecting the Appropriate Diagnostic Mode
The GT60 offers various diagnostic modes tailored for specific tests. Choosing the correct mode is crucial for effective troubleshooting:
- Full System Scan: If the problem is unclear, a full system scan provides a comprehensive overview of your car’s electrical health. This mode checks all major systems—engine, transmission, ABS, and more—for irregularities, offering a holistic assessment.
- Voltage Test: When investigating power delivery issues, the voltage test provides real-time voltage readings on the GT60 screen, typically between 12 and 14 volts. Significant deviations can indicate connection problems or battery issues, warranting further examination.
- Specialized Module Test: For issues suspected in specific systems like the BCM (Body Control Module) or ECM (Engine Control Module), the GT60 allows for individual module testing. This focused approach enhances accuracy in complex system diagnostics.
Step 3: Interpreting Diagnostic Data
Once you’ve selected and run a test, the GT60 will display diagnostic information. While initially it might seem complex, the user-friendly interface helps clarify each piece of data. Here’s what to focus on when reviewing the GT60’s data report:
- Voltage Readings: The scanner shows voltage levels, with healthy circuits generally reading between 12-14V. Readings outside this range suggest potential power supply issues within the circuit.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): The GT60 displays any DTCs along with descriptions, simplifying interpretation. For example, a “P0420” code might point to catalytic converter problems, while “P0300” indicates engine misfires.
- Freeze Frame Data: When a problem is detected, the GT60 captures freeze frame data, including engine temperature and load conditions. This contextual information is invaluable for accurate diagnosis.
Step 4: Saving and Reviewing Diagnostic Reports
A particularly useful feature of the GT60 is its ability to save diagnostic reports. This is especially helpful for tracking intermittent issues over time. Saved reports can be reviewed later or shared with professional mechanics, facilitating smoother repairs in the future.
By following these steps, you can effectively utilize the Foxwell GT60’s diagnostic capabilities. Proper setup and mode selection transform complex diagnostics into an accessible process, enabling you to efficiently identify and resolve electrical problems.
Common Circuit Issues and How to Detect Them
A circuit identification tool like the GT60 can aid in identifying various electrical system problems in your car:
- Blown Fuses: Overloads in a circuit can cause fuses to blow. The GT60’s short circuit detection mode and overload indicator light can quickly pinpoint the source, allowing for direct resolution without extensive trial and error.
- Loose Connections: Corrosion or loose connections can lead to erratic voltage readings. Using the GT60’s voltage mode, you can detect these irregularities and locate connections that need tightening or cleaning.
- Short Circuits: Manually finding short circuits is typically difficult. The GT60 simplifies this with full system scans and abnormal data pattern monitoring, quickly identifying where current is taking unintended paths.
- Damaged Wires: Frayed or broken wires disrupt electrical flow. The continuity test on the GT60 can verify wire integrity, showing if a wire is intact or broken along its length.
Understanding these common scenarios and how to detect them with a circuit identification tool makes managing car electrical issues much simpler.
Safety Measures When Using a Circuit Diagnostic Tool
Working with car circuits requires caution. Here are essential safety tips to follow:
- Turn Off the Car When Safe: Unless the diagnostic test requires the car to be running, always turn off the ignition to minimize risks of shock or short circuits.
- Use Protective Gear: Always wear gloves and eye protection, especially when working near the battery or any live circuits.
- Work in Dry Conditions: Electricity and water are a dangerous combination. Ensure you are working in a dry environment to prevent electrical hazards.
- Double-Check Connections: Make sure probes are correctly connected to the intended points. Incorrect connections can damage the scanner and your car’s electrical system.
Taking these precautions can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
Troubleshooting Common Scanner Issues
If you encounter problems with your GT60 or another circuit scanner, here are some quick fixes:
- Tool Won’t Power On: First, verify that the tool is fully charged or properly connected to a power source. If connected to the car, ensure the car battery isn’t depleted.
- No Readings Displayed: Check that the probes are securely attached and that you have selected the correct diagnostic mode for your intended test.
- Inconsistent Readings: Erratic readings often result from loose connections. Tighten connections and re-verify probe contact points to stabilize readings.
These simple solutions can often resolve common issues and get you back to diagnosing your car effectively.
Glossary of Essential Terms in Car Circuit Diagnostics
- Voltage: The measure of electrical potential difference in a circuit.
- Current: The rate of flow of electric charge through a circuit.
- Resistance: The opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit.
- Continuity: The state of an unbroken and complete path for electrical current.
- Short Circuit: An abnormal electrical path of low resistance, bypassing the intended circuit.
Familiarity with these terms will enhance your understanding of the data provided by circuit identification tools.
Further Resources for Automotive Circuit Diagnostics
For those looking to deepen their knowledge of car circuit diagnostics, numerous resources are available. Online courses, automotive forums, and video tutorials on platforms like YouTube offer extensive learning opportunities to refine your diagnostic skills.
Conclusion
Using a digital circuit identification tool, such as the Foxwell GT60, greatly simplifies automotive electrical diagnostics.
By understanding its functions, following a structured diagnostic process, and selecting appropriate modes, you can effectively troubleshoot electrical problems, saving both time and money. More importantly, you gain confidence in addressing future electrical challenges. With these tools and knowledge, maintaining your vehicle’s electrical system becomes a manageable task, ensuring smooth operation.
FAQs
Is it okay to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in?
Yes, it is generally safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner connected. Many drivers do so to monitor live vehicle data. Ensure the device is securely positioned to prevent distractions or accidental disconnection.
Does OBD2 function when the car is turned off?
Typically, no. Most OBD2 scanners require the vehicle to be in the ‘on’ or ‘accessory’ mode to access and read data. Some scanners might offer limited functionality when the car is off, but live data monitoring usually requires the engine to be running.
What types of problems can OBD2 tools detect?
An OBD2 scanner can detect a wide range of issues related to engine performance, emissions, transmission, ABS, fuel systems, and more. It can identify diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for sensor malfunctions, engine misfires, oxygen sensor problems, and various other faults that impact vehicle health and performance.