Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) programs are increasingly critical in the home health care sector. For Home Health Agencies (HHAs), QAPI is not just a regulatory box to tick, but a fundamental framework designed to elevate the quality of patient care, enhance patient safety, and streamline operational processes. These programs utilize data-driven insights and continuous improvement methodologies to proactively enhance the standards of care delivered within the comfort of patients’ homes.
This article explores the crucial role of QAPI in home health agencies, demonstrating how its implementation can effectively address challenges and significantly improve the quality of care provided.
Understanding QAPI in Home Health Agencies
QAPI, mandated by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), is a data-centric and forward-thinking approach aimed at boosting the quality of health care services, specifically within home health agencies (HHAs). For HHAs, QAPI is particularly vital as it fosters a culture of continuous improvement in the quality of care administered to patients in their own homes, especially under Medicare Part A benefits. These benefits encompass medically necessary skilled care delivered intermittently, such as nursing, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech-language therapy, all prescribed by a physician.
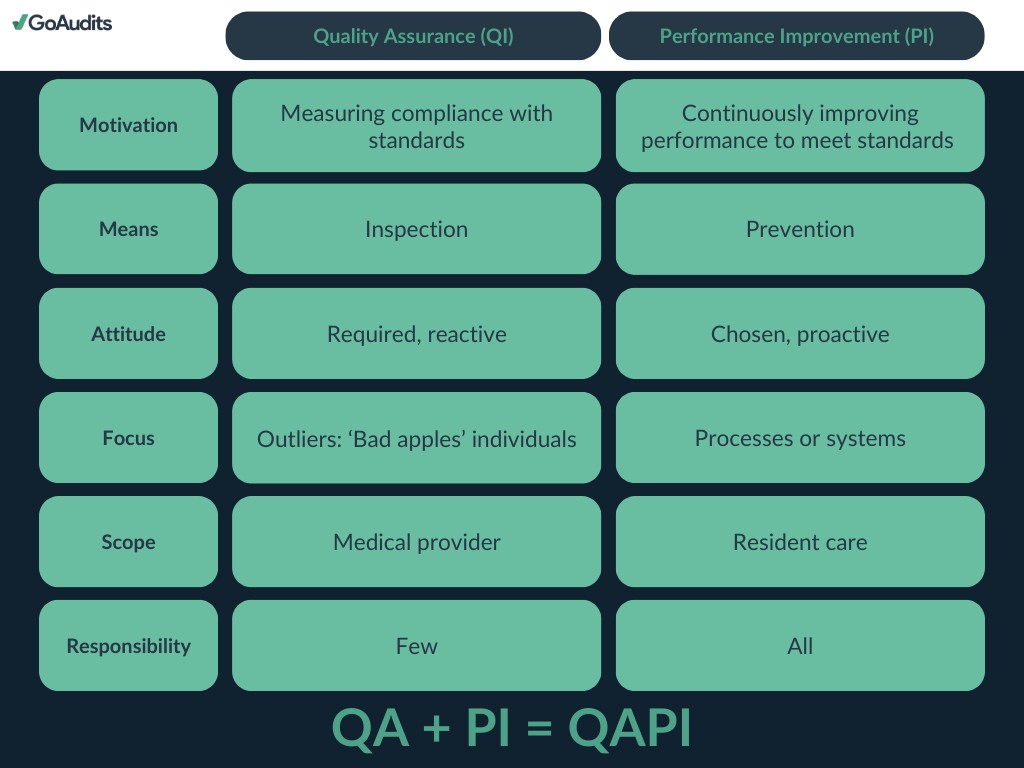
The QAPI plan for home health agencies centers around two core components:
- Quality Assurance (QA): This involves the systematic collection and assessment of data to rigorously monitor the outcomes of care delivery processes. The primary objective is to guarantee that the care provided consistently meets established standards and regulatory requirements. QA activities are instrumental in pinpointing areas where care quality may be lacking and ensuring steadfast compliance with both federal and state regulations.
- Performance Improvement (PI): This aspect concentrates on the methodical enhancement of processes and systems within the agency to elevate the overall quality of care and patient outcomes. PI includes identifying specific areas for improvement, implementing strategic changes, and meticulously evaluating the effectiveness of these changes to ensure long-term, sustainable improvements.
QAPI programs necessitate a comprehensive quality improvement strategy across all levels of a home health agency, from senior management to frontline staff. Agencies are expected to establish clear, measurable goals and leverage data to inform their decision-making processes. This involves in-depth analysis of various metrics, including patient outcomes, patient satisfaction levels, and operational efficiency.
Important Statistic: In 2021, the United States boasted 11,474 Medicare-certified HHAs, serving approximately 3 million Medicare Fee for Service (FFS) beneficiaries. In 2020, a significant 8.3% of all Medicare FFS beneficiaries utilized home health care services.
Given the substantial number of Medicare-certified HHAs and the millions of beneficiaries relying on home health care, robust QAPI programs are indispensable for maintaining high care standards, ensuring patient safety, and driving positive patient outcomes nationwide.
Implementing an Effective QAPI Plan in Home Health
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) emphasizes QAPI as a cornerstone of its broader initiatives to enhance healthcare outcomes, improve patient satisfaction, and optimize cost-efficiency within home health agencies (HHAs).
The CMS has launched the Home Health Value-Based Purchasing (HHVBP) model as a pivotal strategy to incentivize quality enhancement in home health care. This model adjusts payments to HHAs based on the quality of care they deliver, aiming to motivate agencies to improve both the quality and efficiency of their services, with a primary focus on achieving better health outcomes for patients.
Within the HHVBP framework, QAPI assumes a central role. Home health agencies (HHAs) are mandated to implement QAPI programs as stipulated by the Home Health Conditions of Participation (CoPs). HHAs are expected to apply QAPI principles to identify areas needing improvement and to implement strategies to enhance care quality. Agency performance within the HHVBP model is evaluated using a set of quality measures that reflect care outcomes and processes, patient experience, and other pertinent indicators.
Key QAPI requirements for home health include:
- CoP Final Home Health Agency Interpretive Guidance, Effective August 2018
- CoP for Home Health Agencies, Effective January 2018
- Data-driven QAPI program for home health agencies (§484.65)
Utilizing Home Health QAPI Templates and Checklists
GoAudits provides an extensive library of healthcare audit checklists that HHAs can leverage to enhance care quality, ensure patient and staff safety, and improve regulatory compliance. These resources can significantly streamline the implementation and maintenance of QAPI programs.
5 Essential QAPI Elements for Home Health Agencies
CMS outlines five core categories for QAPI programs, commonly referred to as the five QAPI elements or standards.
Learn more about the 5 elements of QAPI in healthcare.
These elements serve as a guide for HHAs to develop, implement, and sustain effective QAPI programs, meeting CMS requirements and driving performance improvements.
- Design and scope
- Governance and leadership
- Feedback, data systems, and monitoring
- Performance improvement projects (PIPs)
- Systematic analysis and action
1. Program Scope: Defining Objectives
- 484.65(a)(1): A QAPI program must be designed to demonstrate tangible improvements in indicators directly related to better health outcomes, enhanced patient safety, and superior care quality. This necessitates focusing the program on areas where improvements are most likely to yield significant positive impacts on patient outcomes.
- 484.65(a)(2): HHAs are required to systematically measure, analyze, and track key quality indicators, including adverse patient events. This involves a thorough assessment of care processes, services provided by the HHA, and overall operations to ensure adherence to desired quality and safety benchmarks.
2. Program Data: Leveraging Information
- 484.65(b)(1): The strategic use of quality indicator data is paramount. This includes data derived from the Outcome and Assessment Information Set (OASIS) and other pertinent sources to effectively shape the QAPI program’s design and direction.
- 484.65(b)(2): Collected data must be actively used to monitor service safety and quality, identify opportunities for improvement, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and ensure the consistent delivery of safe care.
- 484.65(b)(3): The governing body of the HHA must approve the frequency and level of detail in data collection, ensuring that data-driven decisions are integral to supporting the QAPI program’s objectives.
3. Program Activities: Driving Improvement
- 484.65(c)(1): Performance improvement activities should be strategically targeted towards areas identified as high risk, high volume, or problem-prone. This focus should prioritize the severity and prevalence of issues to facilitate immediate corrective actions for any problems that pose a threat to patient health and safety. GoAudits’ incident reporting feature offers a robust solution for real-time tracking of adverse patient events and in-depth analysis of their root causes.
- 484.65(c)(2): These activities must comprehensively include tracking adverse patient events, conducting thorough root cause analyses, and implementing proactive preventive measures to avoid recurrences.
- 484.65(c)(3): Following the implementation of improvement actions, HHAs must rigorously measure success and continuously track performance to ensure that improvements are not only achieved but also sustained over time.
4. Performance Improvement Projects: Demonstrating Progress
- 484.65(d)(1): HHAs are obligated to undertake a defined number of performance improvement projects annually. These projects should appropriately reflect the scope, complexity, and historical performance of the agency’s services and operational activities.
- 484.65(d)(2): Comprehensive documentation of these projects is mandatory, including the rationale for their initiation and the progress achieved. This documentation serves to demonstrate a clear and ongoing commitment to continuous improvement.
5. Executive Responsibilities: Ensuring Oversight
- 484.65(e): The governing body of the HHA holds ultimate responsibility for the QAPI program. This encompasses ensuring the program is well-defined, effectively implemented, and consistently maintained. It also involves addressing key priorities related to quality and patient safety, setting clear expectations for patient safety protocols, and effectively addressing any findings of fraud or waste.
Explore how these 5 QAPI elements provide the structural framework for any QAPI plan, applicable across various healthcare settings, including nursing homes, hospices, and more.
Key Quality-Related Challenges Faced by Home Health Agencies
Home health agencies encounter unique challenges in maintaining high standards of care compared to other healthcare environments:
-
Staff Recruitment and Retention: The home health sector is significantly challenged by difficulties in attracting and retaining qualified personnel. This encompasses not only skilled nurses and therapists but also essential home health aides who provide daily patient care. High staff turnover particularly complicates quality processes and regulatory compliance. Addressing this issue requires focusing on enhanced training programs, competitive compensation and benefits packages, and strategies to improve job satisfaction.
-
Maintaining Quality of Care and Patient Safety: Upholding stringent care standards and ensuring patient safety are of utmost importance. This necessitates developing robust training initiatives, integrating technology for improved care management, and actively participating in quality improvement programs. The individualized nature of home health care demands a strong emphasis on culturally sensitive care and addressing the specific needs of each patient.
-
Patient Engagement and Education: Actively involving patients and their families in care planning is crucial for achieving successful home health outcomes. Educating them on disease management, medication adherence, and preventive healthcare measures can significantly enhance health outcomes and decrease hospital readmission rates.
-
Coordination with Healthcare Providers: Effective communication and seamless coordination with a broad spectrum of healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, specialists, and hospitals, are vital to ensure consistent care continuity. This necessitates efficient information exchange and robust collaboration across different care settings.
-
Navigating Regulatory Compliance and Reimbursement: Home health agencies must navigate a complex web of regulations and compliance mandates. Fluctuations in healthcare laws, Medicare, and Medicaid policies can substantially impact service delivery models and reimbursement structures.
Leveraging Healthcare Compliance Software for QAPI in HHAs
GoAudits’ healthcare auditing app empowers HHAs to conduct comprehensive checks and audits covering patient care, safety protocols, and adherence to care standards. GoAudits simplifies the often complex process of data collection and documentation essential for QAPI programs, offering user-friendly, mobile-accessible auditing capabilities that function seamlessly both online and offline.
Featuring real-time reporting, customizable checklists, and secure, centralized data storage, GoAudits provides valuable tools that help HHAs maintain high standards of care and improve overall operational efficiency as part of their QAPI initiatives.
Core Benefits of Implementing QAPI for Home Health Agencies
Implementing QAPI programs offers numerous significant benefits for home health agencies:
- Enhanced Patient Care Quality: QAPI programs are designed to identify and resolve issues within care processes, leading to improved patient outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies and waste, QAPI programs can assist agencies in lowering costs and enhancing financial stability.
- Improved Regulatory Compliance: QAPI programs help agencies consistently meet all relevant regulations, minimizing the risk of penalties and fines.
- Potential for Increased Reimbursement: Certain payers, including Medicare, offer incentives and rewards to home health agencies demonstrating effective QAPI programs.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: QAPI relies on robust data collection and analysis, enabling agencies to make informed decisions based on concrete evidence and outcomes.
- Proactive Risk Management: QAPI programs aid in identifying and mitigating potential risks, reducing the likelihood of adverse events and enhancing patient safety.
- Stronger Communication and Collaboration: QAPI fosters improved communication and collaboration across various departments and team members, promoting a unified and patient-centric approach to care delivery.