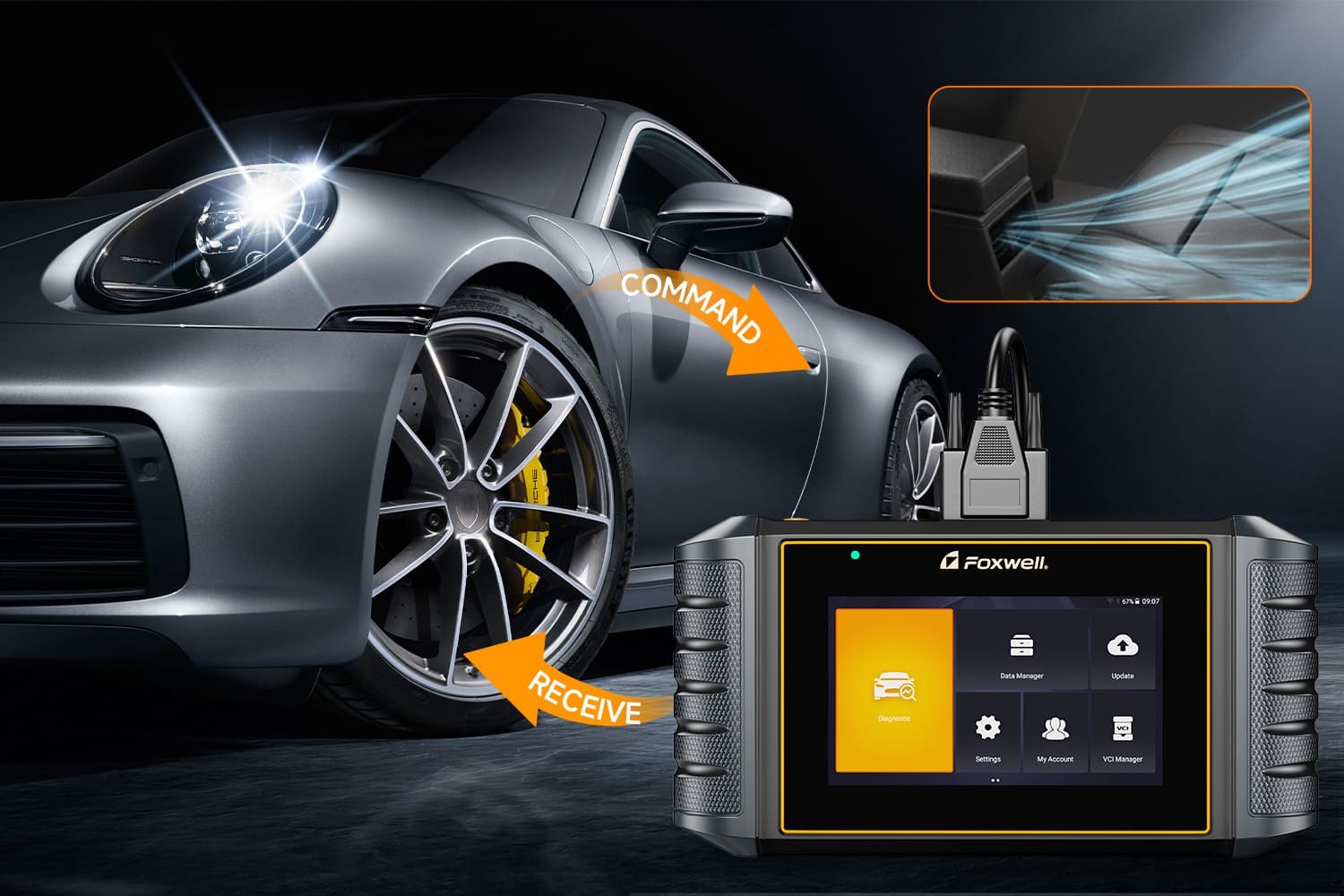
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) port is a standard feature in modern vehicles, instantly recognizable to anyone familiar with automotive repair. This small, rectangular connector is primarily used by technicians to diagnose engine and system issues. However, discussions have emerged about whether its capabilities extend beyond diagnostics, specifically exploring if it’s possible to unlock doors or even start a car engine using just an OBD2 scanner. Let’s investigate this further.
Understanding the OBD-II Port
Since the mid-1990s, the OBD-II port has served as a gateway to your car’s internal computer network; every car manufactured since then is equipped with one. Its main purpose is to allow mechanics to connect diagnostic tools, read trouble codes, and monitor various vehicle systems. Think of it as a health monitor, but for your car!
The OBD-II port has several crucial functions. Primarily, it reads Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), offering valuable insights into potential problems when the “check engine” light comes on. Furthermore, it provides real-time data from sensors, such as engine temperature and speed, which are vital for maintaining optimal vehicle health and performance.
Can OBD-II Unlock Car Doors?
Your OBD-II port is connected to your car’s central locking system, leading to speculation about using it to unlock car doors. While theoretically, sending commands through the OBD-II port might seem possible, it’s highly unlikely to work in practice. OBD-II communication protocols are not designed to send the specific “pop” signals needed to directly activate door locks.
Car manufacturers are acutely aware of potential vulnerabilities and have implemented significant security measures to prevent unauthorized access. Each manufacturer employs unique security protocols, meaning a method that might (hypothetically) work on one brand is unlikely to be effective on another. Modern vehicles utilize encrypted communication between the OBD-II port and the car’s systems, making it significantly challenging for external devices to send unauthorized commands.
Encryption and authentication measures are in place to protect against unauthorized access and actions. Encryption ensures data privacy, while authentication protocols verify that only authorized devices, like professional diagnostic scanners, can interact with the vehicle’s systems.
Can OBD-II Start My Engine?
Your car’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) acts as the central nervous system of the vehicle, managing everything from starting the engine to fuel injection. In theory, communicating with the ECU through the OBD-II port could potentially allow for engine control, including restarting. However, actually starting an engine is a much more complex process.
Most modern cars rely on encrypted signals transmitted from the key fob to initiate the engine start. Without this specific and authorized signal, the vehicle’s immobilizer system will prevent the engine from starting. Immobilizers add an extra layer of security; even if someone were to gain unauthorized access through the OBD-II port, the engine would still not start without the correct key present.
Automotive brands implement constantly updated security protocols designed to thwart hacking attempts. These protocols ensure that only authorized methods can start the engine, regardless of physical access to the OBD-II port.
Security Implications and Real-World Scenarios
Unfortunately, documented cases of hackers exploiting vehicle systems do exist. However, these instances are typically carried out by highly skilled individuals with deep knowledge of specific car systems and often involve sophisticated techniques and expertise.
The automotive industry is actively combating these threats by continuously improving security measures. Car manufacturers collaborate with cybersecurity experts to proactively identify and resolve vulnerabilities. Regular updates to security protocols are implemented to address emerging threats and ensure the highest possible level of vehicle protection.
Utilizing Scanners Properly
A professional diagnostic scanner, such as the Foxwell NT809BT, is invaluable for effectively diagnosing and maintaining your vehicle’s health. These advanced tools are designed to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, display live vehicle data, and perform various system tests. Connecting to the OBD-II port with a scanner provides deep insights into engine performance, transmission issues, ABS systems, and airbag functionality, enabling early detection of potential problems before they escalate.
With features like wireless connectivity, modern scanners enhance diagnostic convenience and efficiency, streamlining vehicle maintenance tasks and saving valuable time.
Conclusion
So, can the OBD-II port be used to unlock car doors or start the engine? Theoretically, perhaps remotely possible in very specific and unlikely circumstances. However, in practical terms, it’s not a realistic scenario. Car manufacturers invest heavily in sophisticated security measures, including encryption and authentication, to protect their vehicles. While the OBD-II port remains a powerful tool for diagnostics, it is not intended, nor is it typically vulnerable, to being used as a backdoor for critical vehicle functions like starting the engine or unlocking doors. Its primary and secure purpose is for vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
FAQs
What is the primary function of the OBD-II port?
The OBD-II port’s main function is for vehicle diagnostics, enabling mechanics to read trouble codes and monitor various vehicle systems for maintenance and repair.
How do modern cars secure the OBD-II port?
Modern vehicles employ encryption and authentication protocols to secure the OBD-II port, ensuring that only authorized devices can access and interact with vehicle systems.
Why do car manufacturers constantly update security protocols?
Car manufacturers continuously update security protocols to proactively address new threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring the ongoing safety and security of their vehicles against potential exploits.